R&D
Pipeline
| Project | Basic Research | Animal PoC | Non-clinical | Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | BLA | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS-401 COPD |
|
Inhalation | ||||||
| HS-101 OA |
|
Intra-Articular | ||||||
| HS-601 DED |
|
Eye Drop | ||||||
| HS-201 Skin Aging |
|
Intradermal | ||||||
| HS-301 Hair Loss |
|
Intradermal | ||||||
| Project | Timeline | Partner | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| HS-X01* | 2023.11~2023.02 |  |
reproduce previous animal test results and progress to out-licensing discussions when the same effective results are obtained (Q1 of 24) |
| HS-401 | 2022.02~ |  |
Joint research on PoC study using COPD patient tissue |
| HS-201/2 | - | Under discussion | Joint development of cosmeceutical substances to generate quick profits |
| HS-101 | - | Under discussion | Joint development with a company that has a leading technology in osteoarthritis treatment |
HS-101
- Cartilage Regeneration and Homeostasis Maintenance (Generation of cartilage > Degeneration of cartilage)
- Improvement of Cartilage Composition (Generation of ECM components and hyaline cartilage)
- Improvement of OA Symptoms (Relieving inflammation and pain)

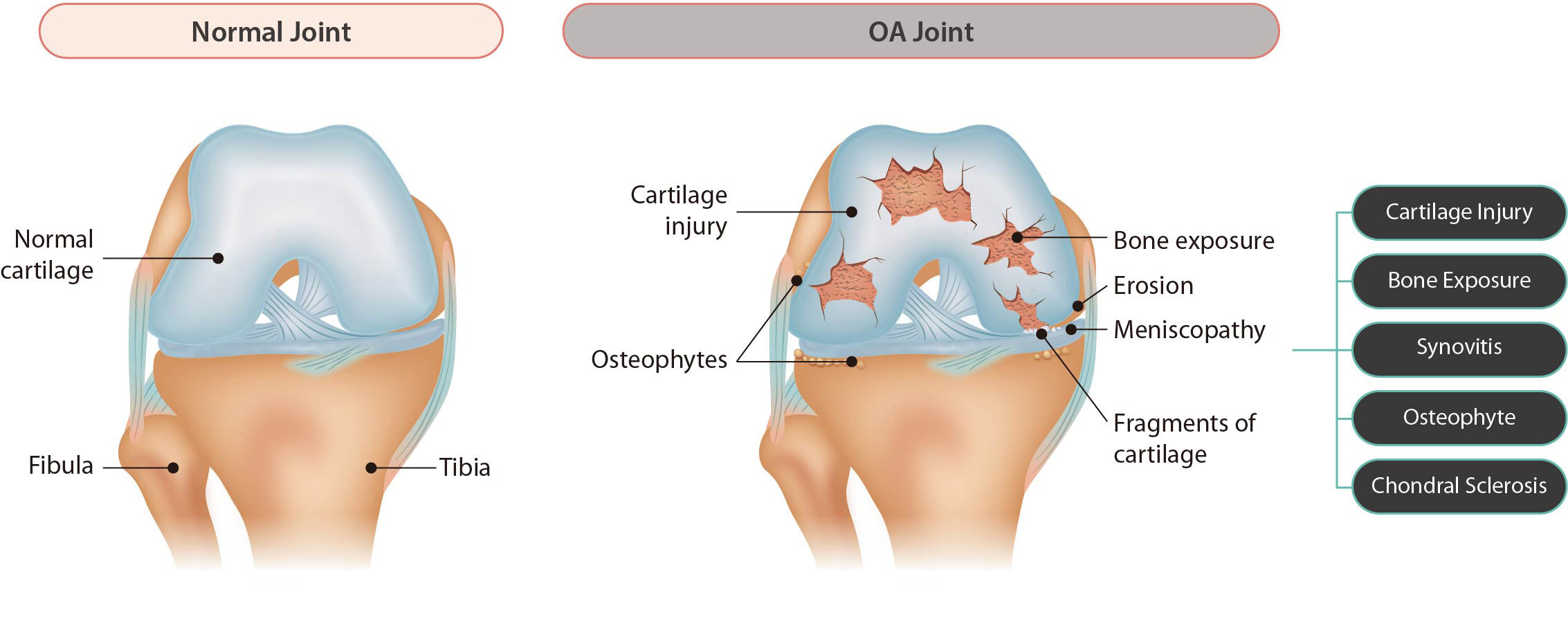
- Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative chronic and inflammatory disease of joint cartilage damage, inflammation, and pain caused by age-related degeneration and/or repetitive trauma.
- More than 300 million patients worldwide suffer from osteoarthritis due to the aging population and the increase of obesity.
- Current treatment is limited to symptomatic improvement from inflammation and pain and there is no fundamental therapy for regeneration and recovery of damaged/degenerated cartilage.
Mechanism of Action
Expected Efficacy
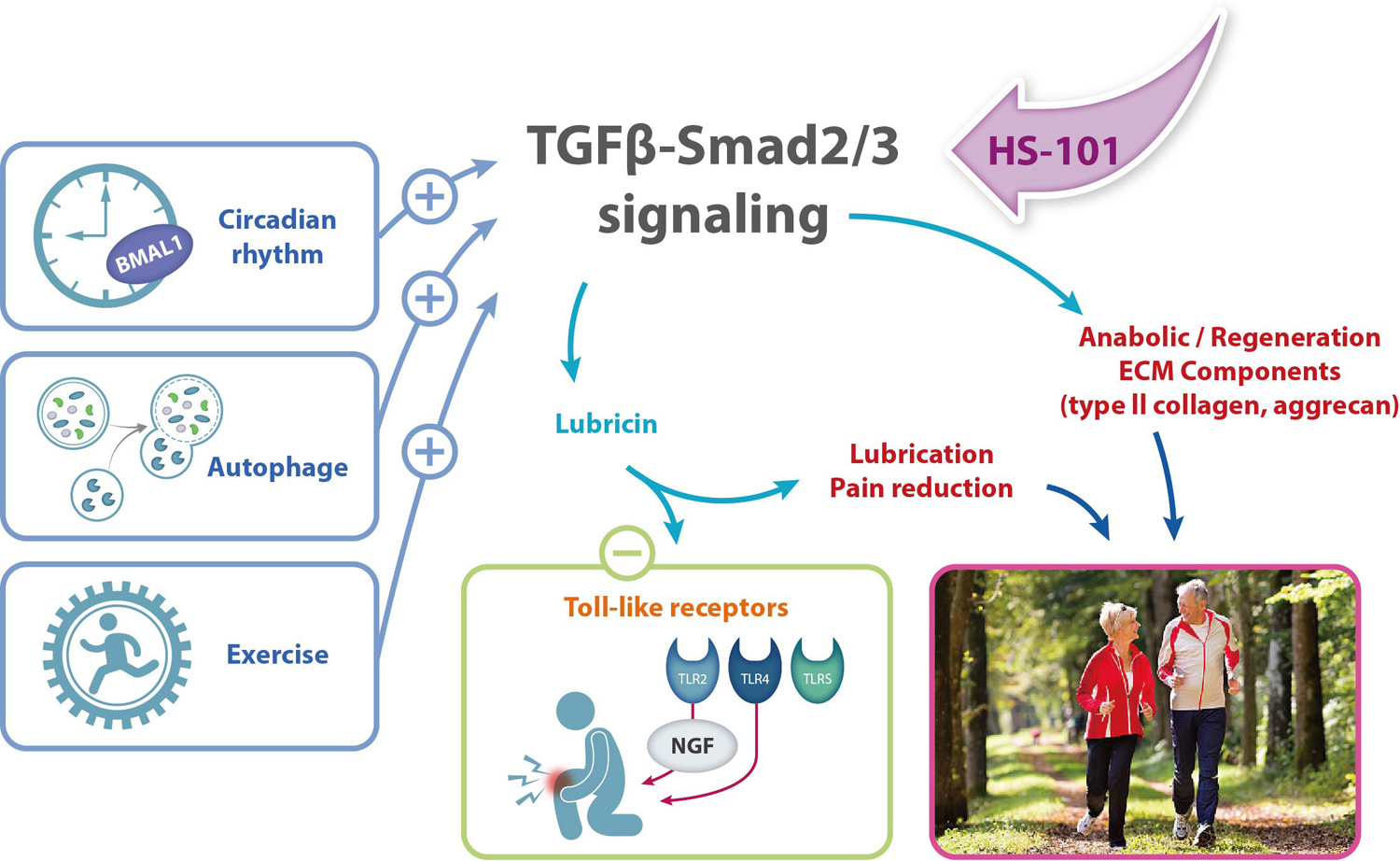
Selective activation of Smad2/3 signaling pathway
Efficacy in OA symptom relief and cartilage recovery
Under development as a promising DMOAD (Disease-Modifying OA Drugs) candidate
- Suppression of inflammation and degeneration caused by smoking and fine dust, etc.
- Regeneration and recovery of Alveoli and bronchial tissue (Increase and activation of the receptors involved in tissue regeneration/recovery)
- Normalization of lung function (Promoting and normalizing the synthesis of damaged/reduced elastin fibers, etc.)

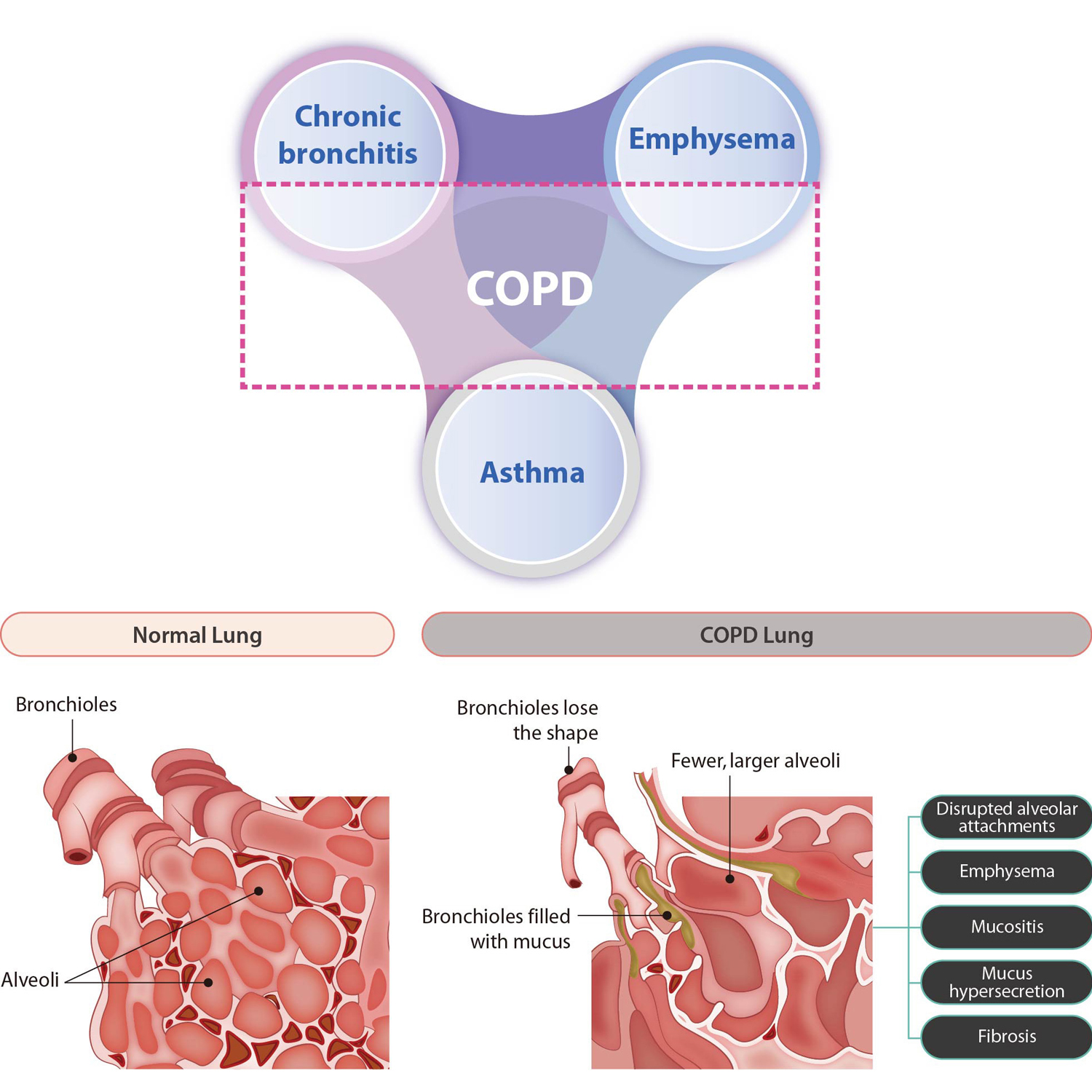
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a respiratory disease that causes obstructed airflow, accompanying pulmonary tissue damage and abnormal inflammatory response. Aging and smoking are the most common causes of COPD.
- It leads to multiple complications such as emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma, and pulmonary hypertension
- As current COPD treatments only focus on symptomatic relief such as reducing inflammation and bronchial dilation, there is no fundamental treatment that can regenerate and restore damaged pulmonary tissue.
Mechanism of Action
Expected Efficacy
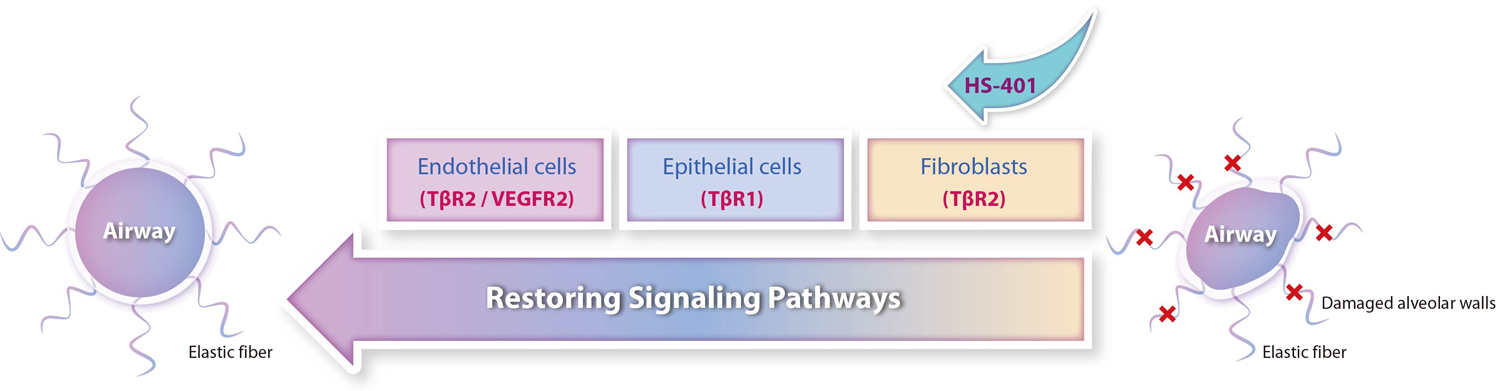
Induce the restoration of regenerative capacity by the synthesis of normal elastin fibers in alveoli and bronchial tissues and by the promotion of self-assembly
Under development as a promising fundamental therapy by inhibiting chronic inflammation and airway obstruction, as well as normalizing lung function through tissue regeneration
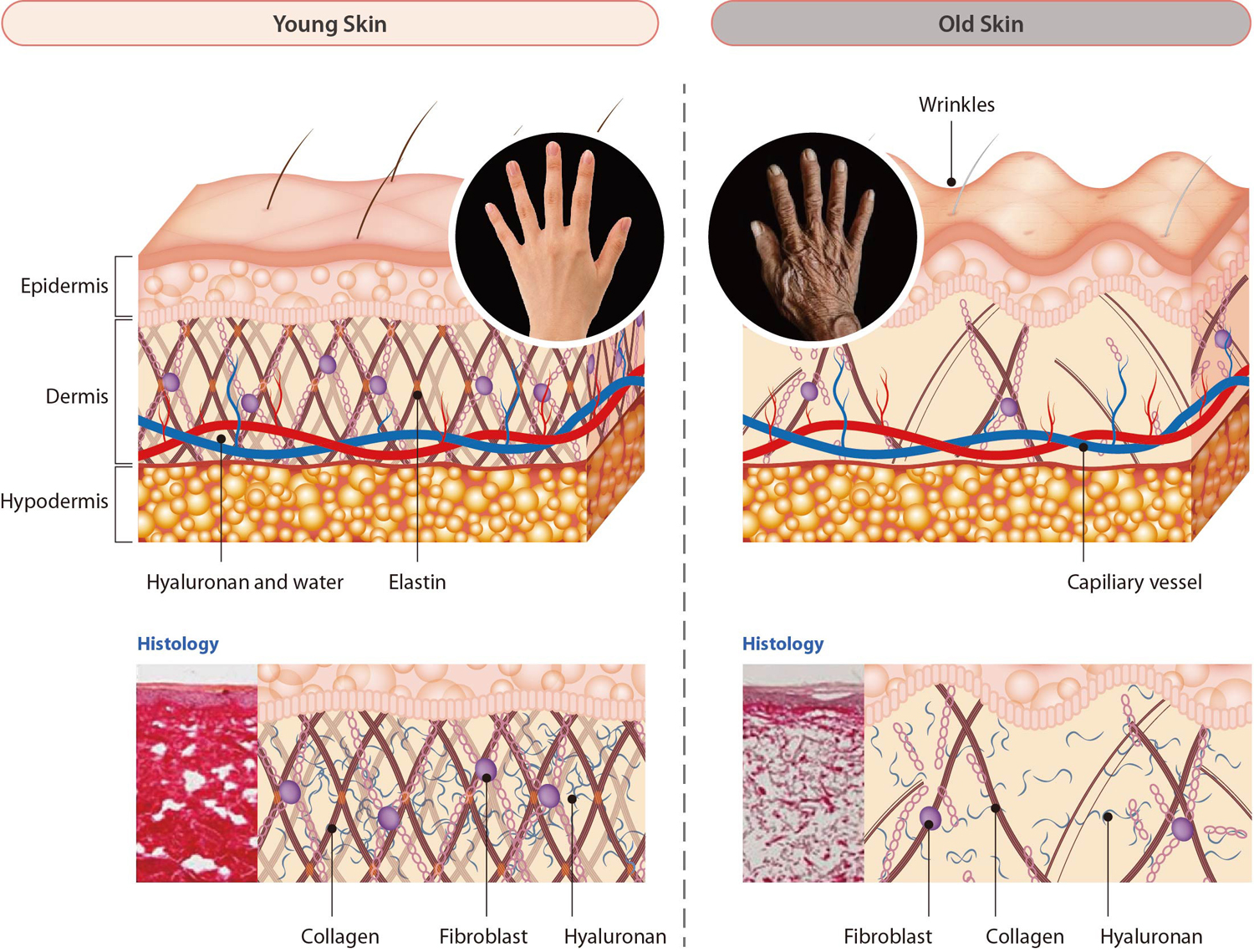
HS-201
- Improvement of skin wrinkles caused by gradual loss of skin extracellular matrix due to aging and exposure to sunlight
- Dual effect of promoting synthesis and inhibiting degradation of hyaluronic acid and collagen, based on cell biological mechanisms of aging
- Skin rejuvenation effect by inducing ECM restoration and strengthening through normalization of aging and damaged skin cells
- Strong efficacy in inhibiting chronic inflammation and reversing aging-associated degeneration through amplification of the communication and crosstalk between ECM and cell.

- As skin aging and degeneration progresses, the content of collagen and hyaluronic acid, which are major components of the extracellular matrix, is decreased, and the need for rejuvenation of the skin tissues that lost elasticity and wrinkled is increased.
- With the aging population and increasing interest in improving the quality of life, the global medical/esthetic market continues to grow at a rate of over 10% and is expected to reach $15.9 billion in 2025 1).
- Products currently used in facial aesthetic treatments still have concerns about downtime and side effects due to the procedure, and the need for innovative treatments with safer and long-lasting natural improvement to replace them is increasing.
Mechanism of Action
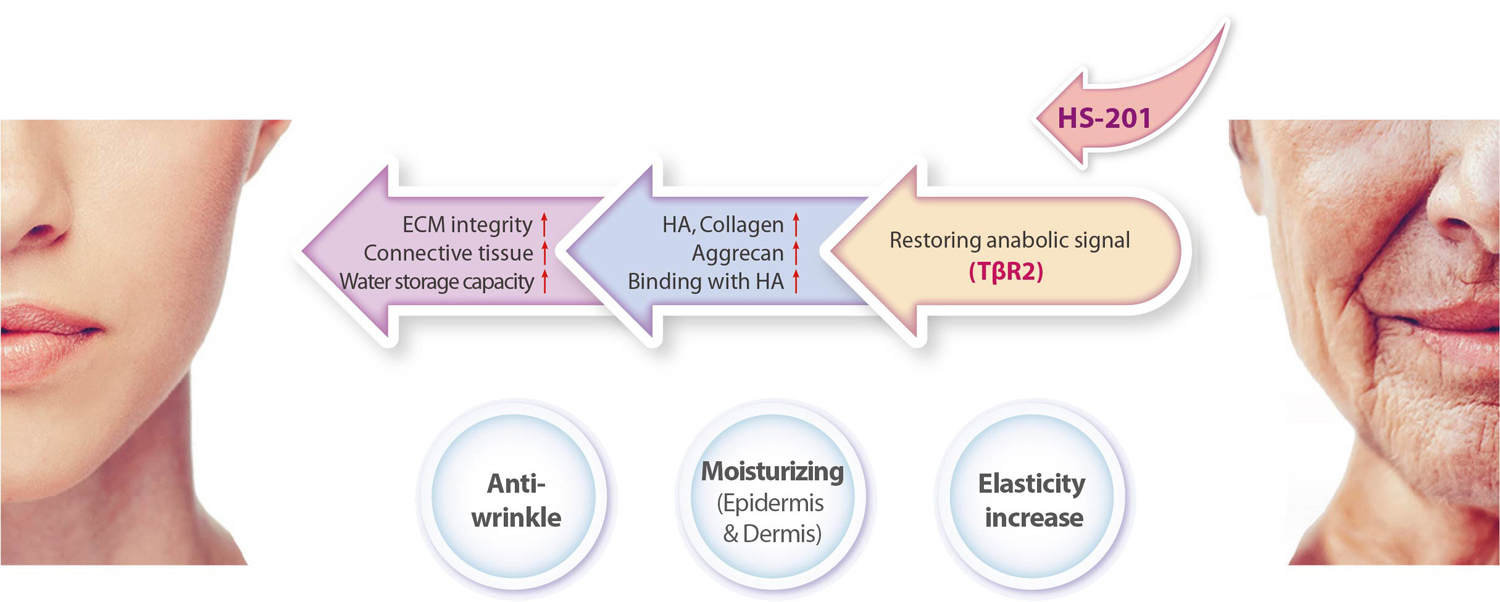
Expected Efficacy
Normalizing damaged and reduced skin cells/tissues due to aging by strengthening the extracellular matrix through the cell biological aging mechanism
Improvement and treatment of aging skin such as wrinkles expected by strengthening the extracellular matrix and normalizing senescent cells
Regeneration and restoring effect based on the biological mechanism on aging skin that lost elasticity and wrinkled due to natural aging and exposure to light
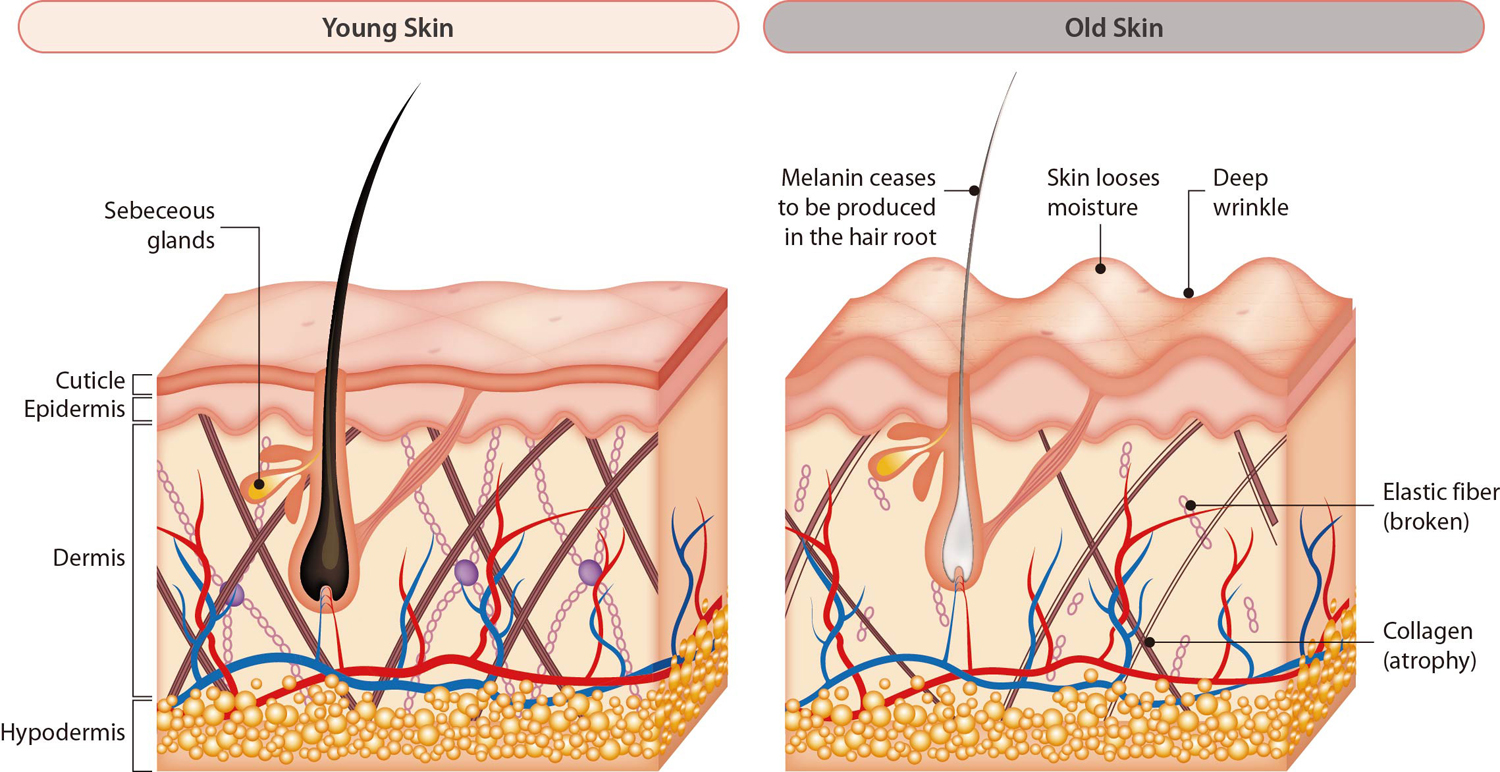
HS-301
- Promotion of proliferating hair growth cells and growth effect utilizing HAPLN1, an endogenous protein specifically expressed in hair growth phase
- Promoting TGF-beta signaling-dependent proliferation and growth-inducing effects of Human Hair Germinal Matrix Cells (HHGMCs) which are directly responsible for hair growth
- Beta-catenin-dependent signaling activation which plays a central role in creating the hair follicle environment
- A complex mechanism and strong hair growth effect through amplification of the ECM-to-cell and cell-to-cell crosstalk

- Hair loss (Alopecia) is a disease caused by aging, stress, and environmental factors, and the number of people suffering from hair loss worldwide is estimated to be over 300 million1).
- The currently available treatments are mainly for male hair loss, and there are still many needs for improvement in terms of efficacy and persistence as well as multiple side effects.
- A drug applicable to various types of hair loss, and having good efficacy on the basis of biological aging mechanisms with not or very few side effects is on the market need.
Mechanism of Action

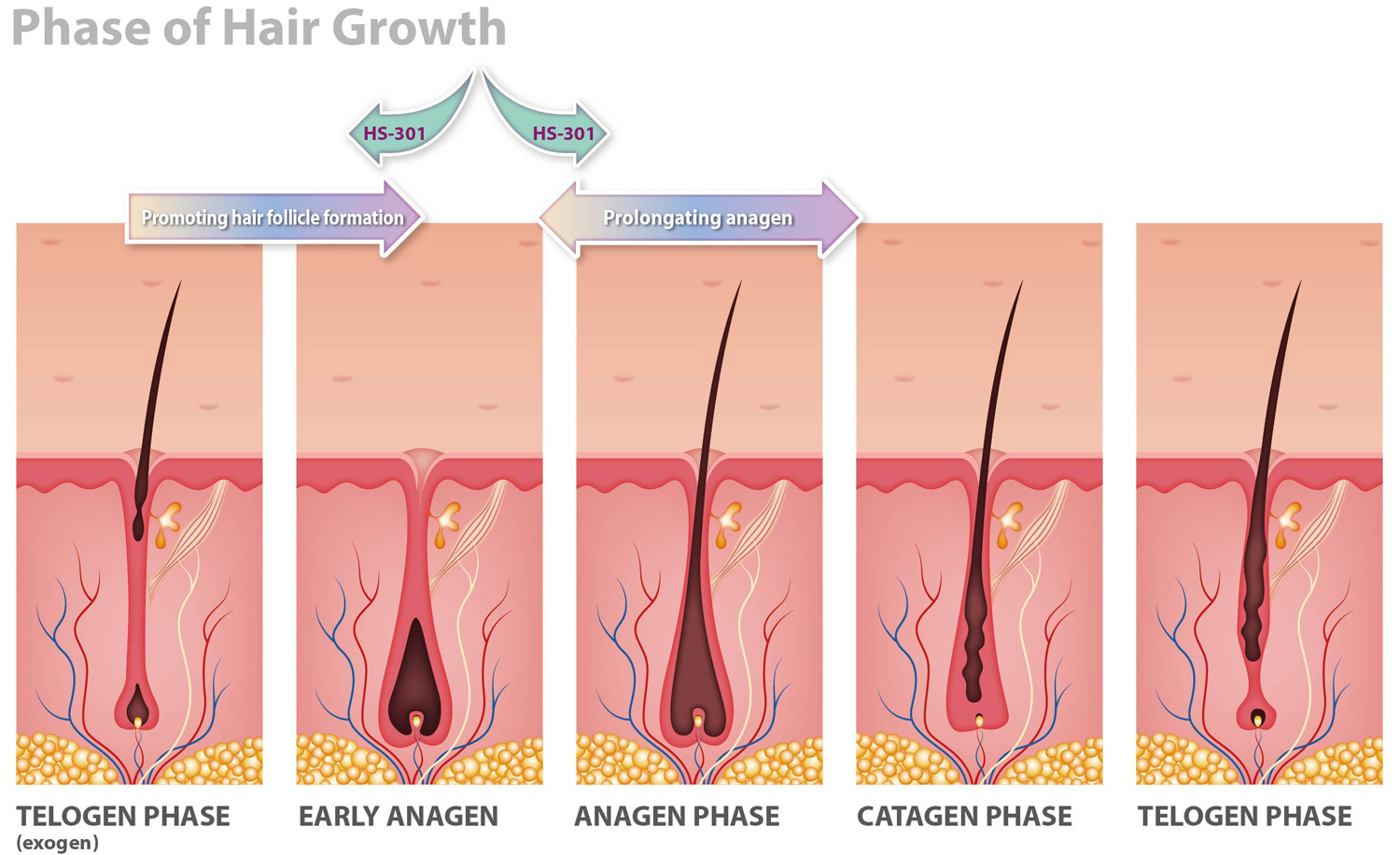
Expected Efficacy
Improvement in hair loss of various causes by restoring degenerative/damaged extracellular matrix in hair follicles
Restoring the signaling pathways in HHGMCs with HAPLN1 that is highly expressed in the hair growth phases
Developing as a hair loss treatment applicable to hair loss of various causes such as aging, stress, and hormonal abnormalities
HS-601
- Inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators (Inflammation mitigation)
- Antioxidant effect (Better recovery of tissues and prevention of tissue damage)
- Tissue regeneration (Wound recovery)
- Increased mucin secretion and moisturizing effect (Protection of eye layer)

- Dry Eye Disease is a condition where the tear film homeostasis on the surface of an eye is destroyed due to aging, external factors, etc.
- Observable symptoms include tear film instability, hyperosmolarity, inflammation of the ocular surface, and neurosensory abnormalities and damage
- Currently, the only treatment in existence is symptom relief products such as artificial tears, That's why there is a need for a more safe and effective treatment that can fundamentally treat the symptoms of dry eye syndrome and minimize patient discomfort..
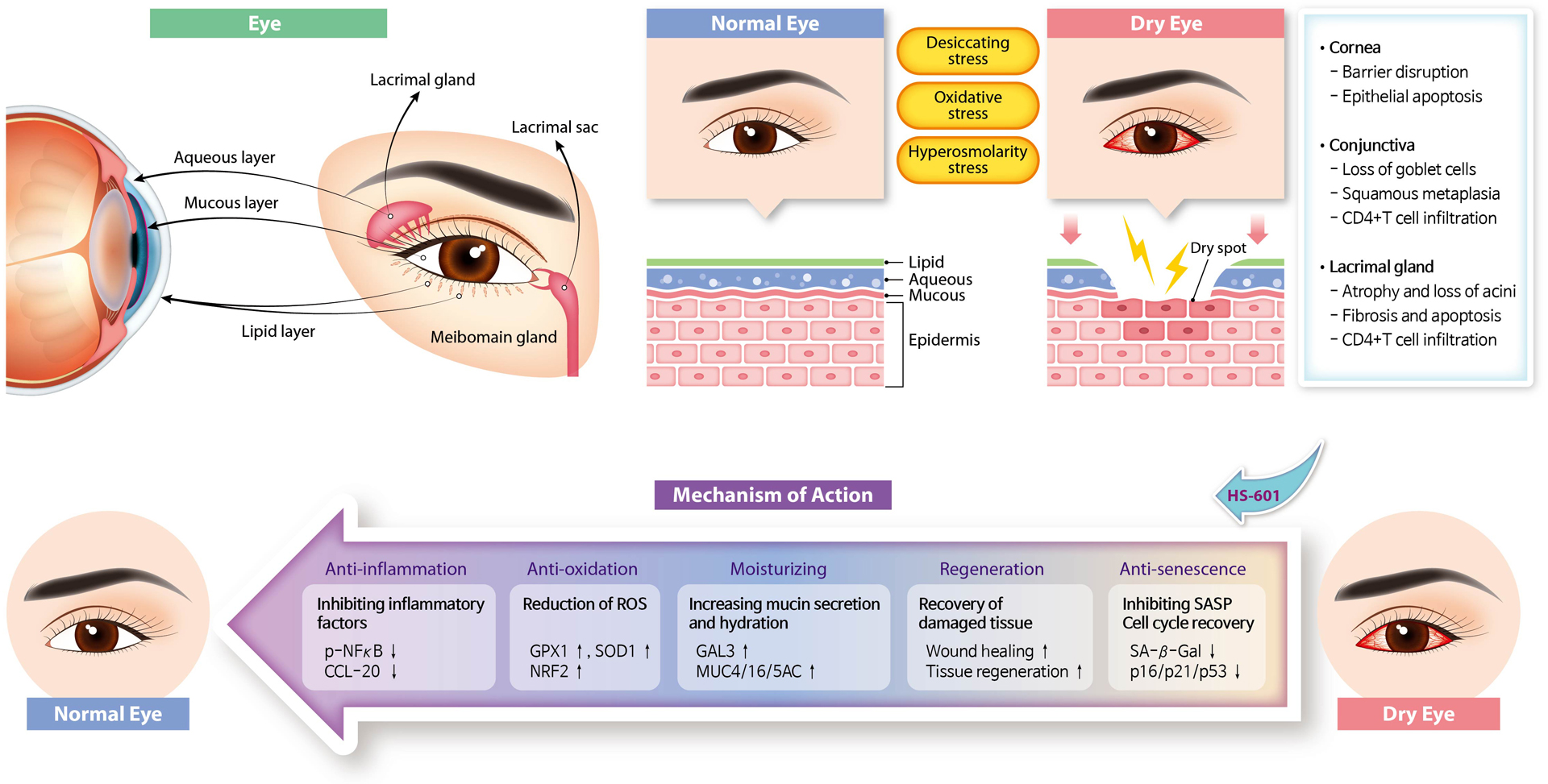
기대 효능
By increasing the mucin secretion in the damaged eye, it inhibits the loss of moisture and augments HA to improve moisturizing effect
Forms an anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative environment by regulating the levels of particles directly linked to inflammatory reaction and oxidation reaction
Restores the damaged ocular tissues by promoting tissue recovery action
Inhibition of ocular cell aging (senescence) through the regulation of molecule levels in aging factors and restoration of cell cycle